
If you’re actively managing your website, you're probably familiar with the dreaded status message in Google Search Console: Crawled – currently not indexed. This can be rather annoying if on your part you are trying to produce quality content for the end user but your pages are not indexed by Google. Its appearance suggests that Google has visited your web pages at least once but for some reason has chosen not to include in its index. If your page is not indexed you are not going to show up in search results and this means that even if there is a lot of traffic being driven by Google, your site would not get a chance at that traffic.
If a page is crawled but not indexed, it means while Googlebot has visited and gone through your page, it does not think it is important enough to index. This can have a huge impact on your SEO as no pages may rank for a keyword or appear in the SERPs at all if they are not indexed.
This post will provide complete information regarding what's crawled – currently not indexed and why it happens along with a detailed look at how to address crawled but not indexed pages in Google Search Console. We will also discuss other related issues including discovered – currently not indexed, and provide recommendations for webmasters and SEO practitioners on ways of optimizing their pages to enable Google to index such pages.

Many factors can cause Google to crawl pages but fail to index them as we are going to see in this article. Understanding these reasons is key to fixing the problem:
Google also tends to skim through web pages that have low-quality or in other words, thin pages. This could mean that pages with minimum textual contents, limited hierarchical depth of information, or contents which do not meet the user’s purpose and need.
Google wants to avoid showing similar or practically the same content in the search results. If your page’s content is duplicate to other pages in your website or there are similar pages on the internet, your page will not be indexed.
Google allocates every site some crawl budget, the number of pages to crawl in a given time. Important pages will be crawled and indexed no matter how large your web site is, but some of the less important pages may be crawled but not indexed.
On occasions, the new published pages may remain for sometime before getting into the list of indexed pages. It is possible that Google will index them fast but keep on stalling the indexing process.
Googlebot doesn’t index a Web url after indexing if due to technical imperfections in a website, page takes time to load or server response is low or there are rendering issues. It is also important that during the visit to Googlebot, the page may not be properly loaded and therefore the page may not be indexed. It also affects pages with JavaScript rendering problems, or where their contents rely heavily on ‘client-side’ processing. To help Google index your site properly, you need to have a fast stablished server and clean source code.
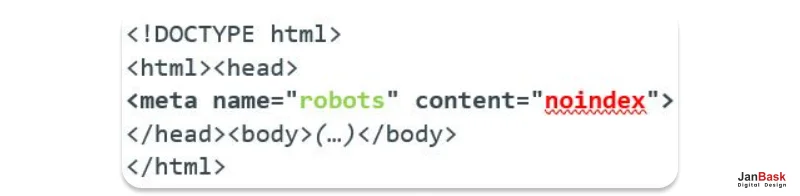
If you have a noindex meta tag or HTTP header on such a page, you tell Googlebot not to index your page directly. It is sometimes inserted purposefully during development or applied to the wrong pages . Be sure again of the use of noindex instructions on the pages that are to be intentionally omitted, for example internal search results or certain administrative pages.
Google has recently introduced mobile-first indexing, and that is why your site’s mobile version is a priority for indexing and ranking. If the page is not friendly to mobile devices, maybe slow to load or having poor user experience on a mobile or is nonresponsive, then it may be crawled but not indexed. Responsive web design is critical for your internet pages to be considered when a search query is conducted.
Google utilises internal links to navigate through your website and understand the importance of different pages. If a page is not well connected on your internal network, it may not be considered very valuable and thus may just not be indexed. This problem is common with pages that are located in the structure of your site or those that few internal links connect them to.
At times, the robots.txt file may prevent some pages from being indexed by search engines by containing wrong rules or patterns. Although it can and does crawl a page specified by robots.txt, Google may not index such a page as it complies with the guidelines that prohibit crawling. This omission can be avoided by often conducting a check up on your robots.txt file.
An orphan page, also known as a lonely page, is a Web page that doesn’t receive any links from other pages within the website. Unlinked, or orphan, pages remain hidden both from the user and Googlebot. However, if Google finds them through other methods, for instance, a sitemap, but they are not well incorporated into your site map as internal links, then they are likely to remain unindexed as irrelevant.
Over-optimization includes uses of keyword stemming, over-reliance on SEO techniques or producing illiterate content. Google’s algorithm is able to notice such problems and may choose not to consider the change at all if Google feels that the page is over-optimization for better search rankings. To avoid this problem, it is crucial to keep your SEO techniques organic and center them on the user.
If your website contains pages designed solely for affiliate links with little original content, Google may decide not to index them. Pages that are purely designed to generate commissions without offering much value to users are often filtered out by the search engine.
Google works to ensure that search results offer valuable, trustworthy, and relevant information to users. Pages that are overly spammy, filled with irrelevant content, or loaded with advertisements may be crawled but not indexed. Pages should focus on delivering high-quality, user-centered content that meets search intent.
Looking for SEO Services? Fix the 'Crawled - Not Indexed' Issue Today!


Crawl – currently not indexed is not a position that you should sit back and watch; it is a signal that you must do something about it when you find your site in the Google Search engine. Here are the steps you can follow to do away with this issue and also make Google index your pages.
One of the key success factors to determine whether Google will index a page or not is the content quality. Google has a preference in the indexing of pages that are useful to users through unique, informative and proper formatting. Here's how to improve your content quality:
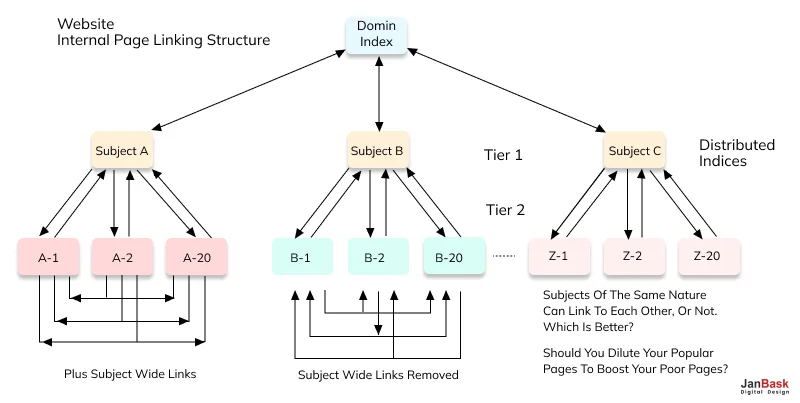
This is primarily very important since internal linking can help Google crawl and index your pages effectively. Web pages that are interconnected in your website are likely to be indexed because Google considers them more relevant. Here’s how to strengthen your internal linking:
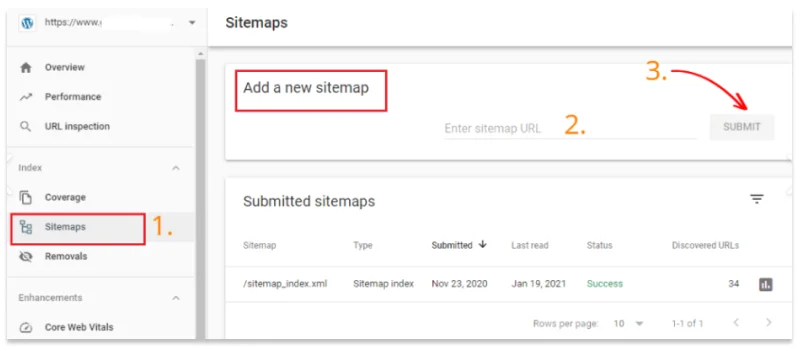
Crawling is not necessarily followed by indexing in Google, but the latter can be initiated through Search Console, entering the desired web page address in the search bar. Here’s how:
When people are searching for your website, a number of technical factors like broken links or server response issues may wipe out the web-pages from Google index in spite of the fact that it is crawled. Fixing these errors is crucial, lets see how:

There might be some pages that you wish to have indexed but that have noindex tags which means it might be crawled by Google but will not be indexed. Here’s how to fix this:
Each of these methods addresses specific issues that could be preventing Google from indexing your content, ensuring that your hard work in creating quality pages pays off in improved search engine rankings and traffic.
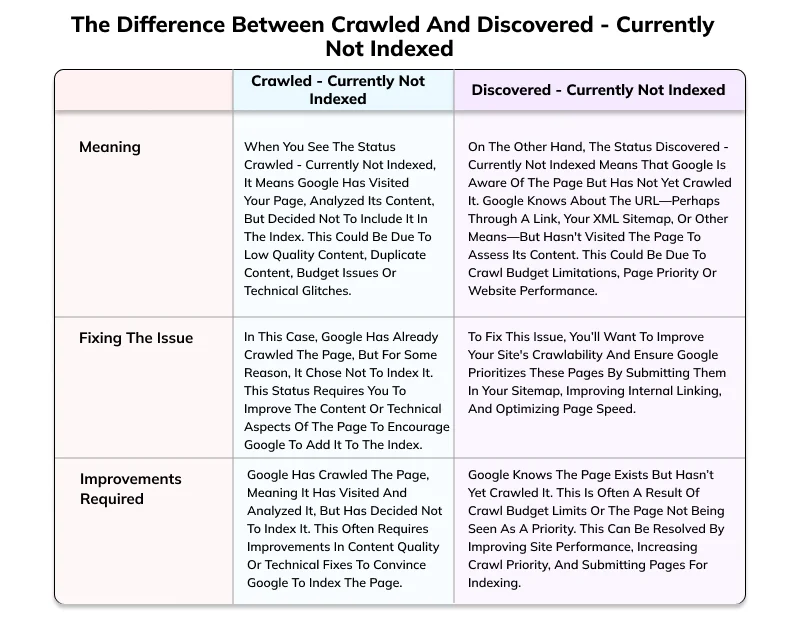
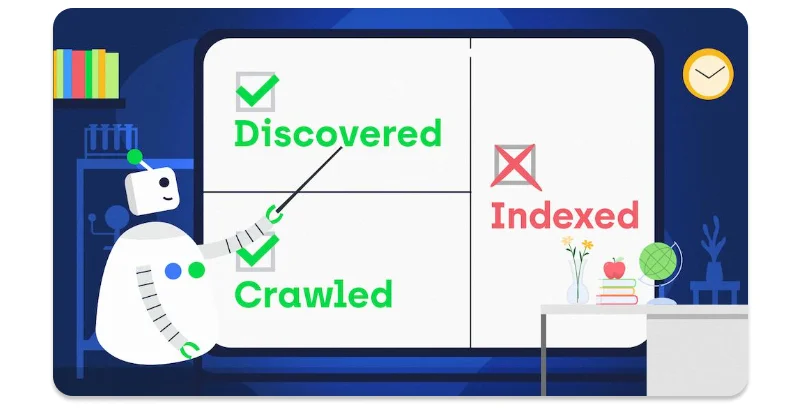
Understanding the distinction between crawled - currently not indexed and discovered - currently not indexed is key to diagnosing indexing issues in Google Search Console. Although these two statuses might seem similar at first glance, they represent different stages of the indexing process.
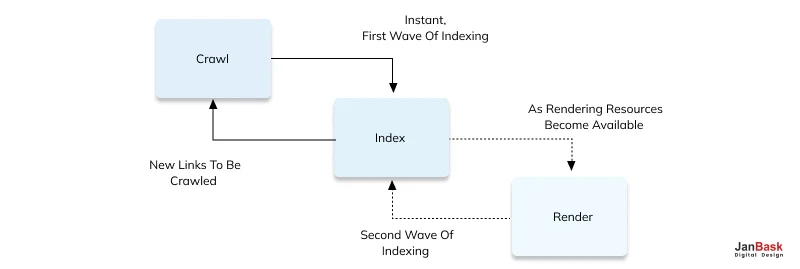
For more SEO technical optimization, consider the following:
A. Optimize Site Performance
Improve page load speed: Rarely, you may find that a particular page causes slow loading, easily found with the help of tools like Google PageSpeed Insights.
Compress images: High size images should be avoided since they impact the loading time of a site, choose formats like WebP.
B. Use Structured Data
META keywords guys, adding schema markup can make it easier for search engines to comprehend what your pages contain and this may force Google into indexing them.
C. Fix Robots.txt Errors
Make sure that you do not have some pages in your robots.txt file that are actually telling Google not to crawl or index at all.
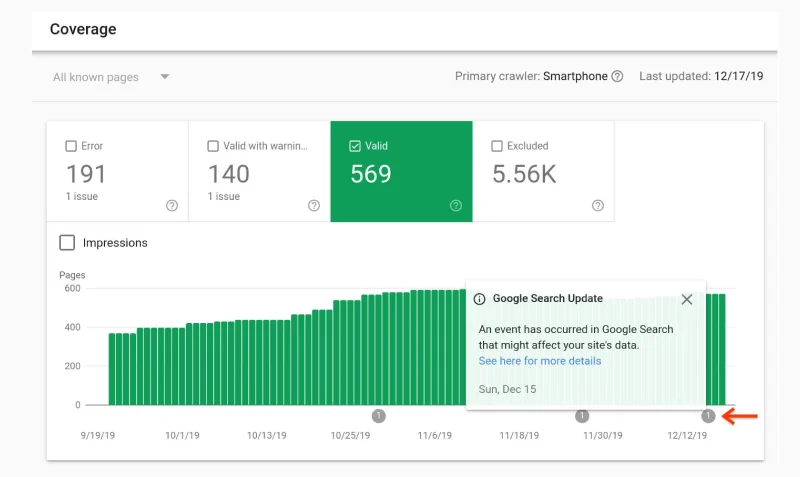
The Index Coverage Report in Google Search Console is one of the most valuable resources to any webmaster and SEO expert. It gives comprehensive information about the manner in which Google is communicating with your site, particularly the comprehensiveness of its crawl and index of your Web pages. Using this report, you can get an idea of the general well-being of your site, in terms of SEO and identify why specific pages are not indexing in the search engines.
Due to the fact that this report has several categories, you can evaluate whether there are those web pages which are well indexed and those which have problems that should be solved. Here’s a breakdown of the key elements:
The part of the report, which is given below, embodies all the pages that Google has visited and then chosen to index. These pages are able to rank in Google search and can therefore be seen by a user that is searching for a keyword. On this category pages, content, structure and technical optimisation are usually well done.
What to check: Make sure the high impact pages are here, such as the home page, check point pages, product specific pages, and blog posts. The absence of a distinct set of key pages requires further investigations in order to determine why it did not index the page.
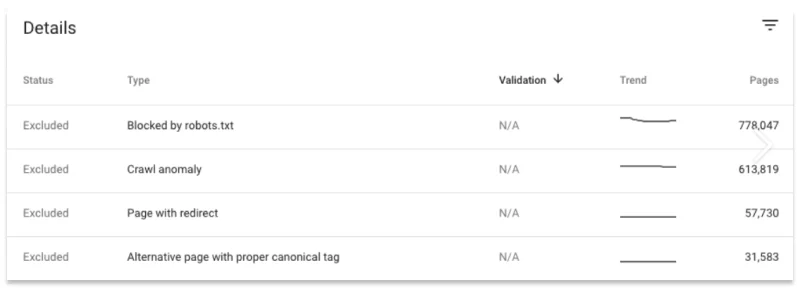
The excluded section shows the pages that Google has crawled but excluded from its index for various reasons. These reasons can range from intentional exclusions, such as noindex tags or duplicate content, to unintentional exclusions caused by technical errors. Common causes for pages being excluded include:
What to check: Check this part frequently to make sure certain pages are omitted on purpose. Lack of crawl budget can be devastating to your site, especially if vital pages are not getting crawled because of technical problems or perhaps deliberate noindexation.
This section is brought by Google to show the pages that Google has visited and continues to visit but has not yet included in its index. This means that Google’s crawlers have been to the page and examined it for relevance only to conclude that it is not relevant enough to join the search index.
What to check: Use this section to identify pages that have been crawled but not indexed, then review them for potential improvements in content quality, performance, or SEO optimization. This section can signal that further optimization is needed to ensure indexing.
This section demonstrates various URLs found by Google but not yet indexed by Google Bot. Google knows these URLs exist (from a sitemap or external link) but hasn’t evaluated the content because:
Even if your website has a lot of pages, Google can avoid crawling these pages for a certain period if its crawl budget was used to crawl other pages within your site.
Google may decide not to visit pages offering content which in its view is low value or importance, few content or bad intranet link.
What to check: Improve the internal linking or submit a new sitemap to Google, or even use the URL Inspection tool to ask for indexing manually.
It’s important for you that the Google search engine takes your web pages into its lists and displays them with enhanced rankings. To ensure that all your pages get crawled and indexed follow these best practices which are outlined below.
Google majors on the fact that it only indexes those pages that are beneficial, fresh and possess quality information. Such kinds of pages are most likely to be indexed because search engines consider them as beneficial to the users. To achieve this:
This means internal links assist the Googlebot in crawling through your site making it easier for the crawlers to find the pages.

What this means is that Google has crawled your page, but not yet said it’s ok to index it and therefore the page isn’t present in search results.
For example, the problems can be fixed by fixing the page content, internal link, crawl error checks, and submitting URL for indexing in Google Search Console.
For pages with low content quality, or duplicate content, or that take forever to load, or are simply marked noindex, perhaps yours won’t get indexed.
Google discovered means Google knows about the page but hasn’t crawled it yet. If the page has been crawled technically but not indexed, then the page status is CRAWLED.
Indexing times can vary. Indexed pages may take several weeks or days to be indexed, depending on things like your site crawl budget and content quality.
Google doesn’t force you to index a page, just like you can’t force Google to rank a page, but you can request Google to index your page using Google Search Console and give you to ensure your page is indicative of indexing.
Following these best practices makes your website more crawlable and much more likely to be indexed by Google and become visible to search users. While consistently there are the latest SEO trends and Google's updates, it is equally essential for your future SEO performance and higher ranks that Google correctly crawls and indexes your most vital content. When you use JanBask Digital Design, you get a team of SEO resources that continuously refresh strategies according to the most recent best practices. Not only do they help you optimize your site for better Google indexing, but they also provide comprehensive monitoring and analysis to keep you and the SEO performance of your site as it moves. With their expertise in latest tools and methods, JanBask assists business entities in increasing their effectiveness online for steady development and search engine ranking outcomes. With this approach to their SEO services, it is possible to find out that every process of SEO is well optimized, from technical optimization to content optimization.
Fixing the 'Crawled - Not Indexed' Issue in Google Search Console!

Leave a Reply