

Have you ever thought about “gutting out” your website to reveal its flesh and bones?
“Why is that even necessary?” you may wonder.
Well, the devil lies in the details. And your website’s devil may be hidden in its skeleton or source code. No matter how you’re associated with your website- whether as a coder, web designer, digital marketer, or even business owner-” View Source Code” is one command that can change your life forever. Online, at least.
Your source code may be dragging down your SEO, user experience, page load speed, and, ultimately, your online revenues! If gone unchecked for long, potential malware could be lodged deep within your lines of code, secreting poisonous effects on your website’s performance. We do not wish to scare you, but this horror could become a reality unless you learn to view source code independently and as often as possible!
What is source code?
How do I see the source code of a website?
How do I view the HTML code of a website?
If the questions above have already begun buzzing around, you’ve arrived at the ultimate resource to get them answered. This blog will deliver comprehensive information on source codes, how they work, and how to leverage them to your advantage. Expect this information in simple language to enrich you with all the technical stuff minus the confusion. Ready to learn? Let’s go!
Follow the instructions below, and you should be able to effortlessly view the source code of your desired page or website.
Alternatively, you can press F11 in Windows, which will work on most desktop and laptop models.
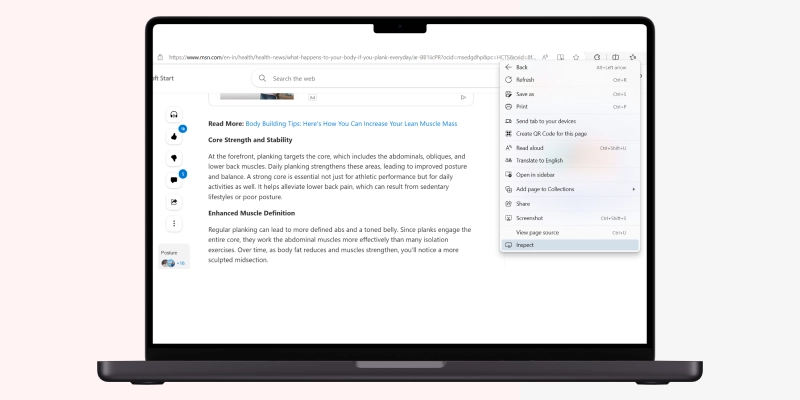
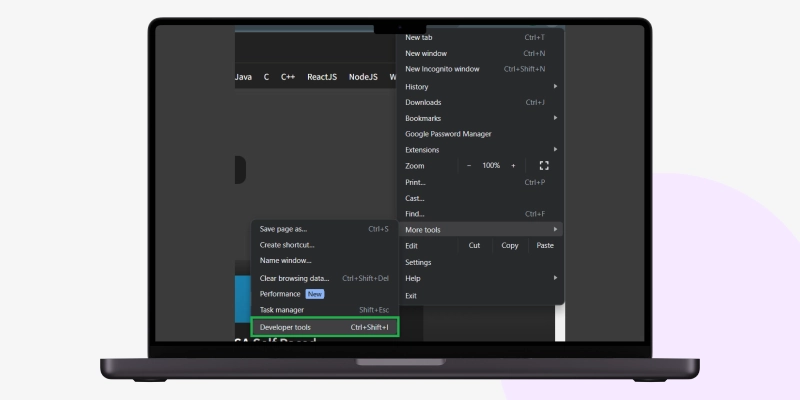
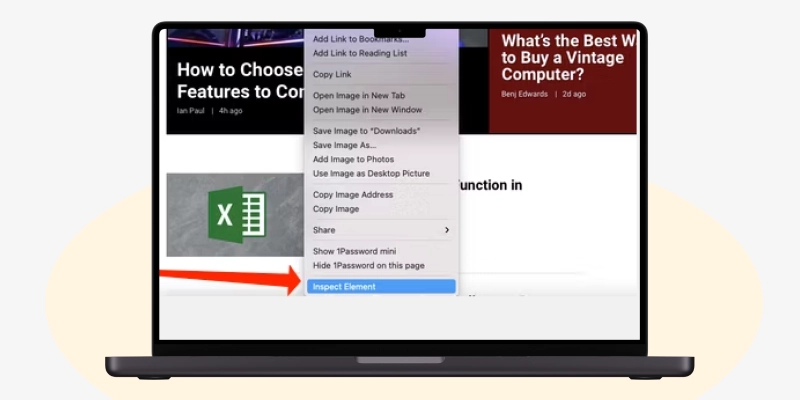
Select the “Control + Shift + I” keys to view the page source through the keyboard and open the Edge developer tools section.
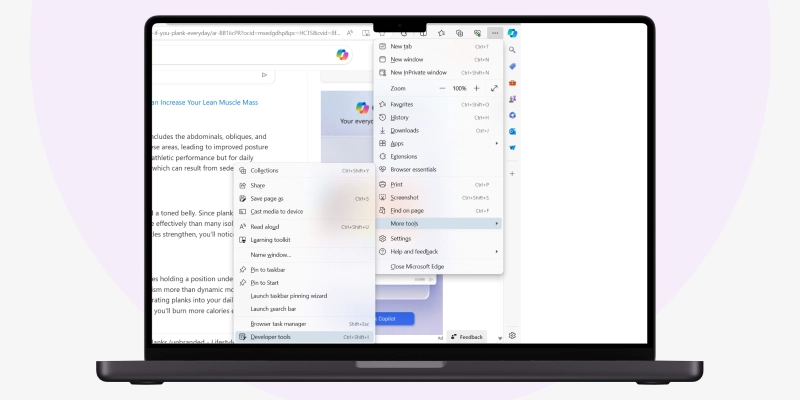
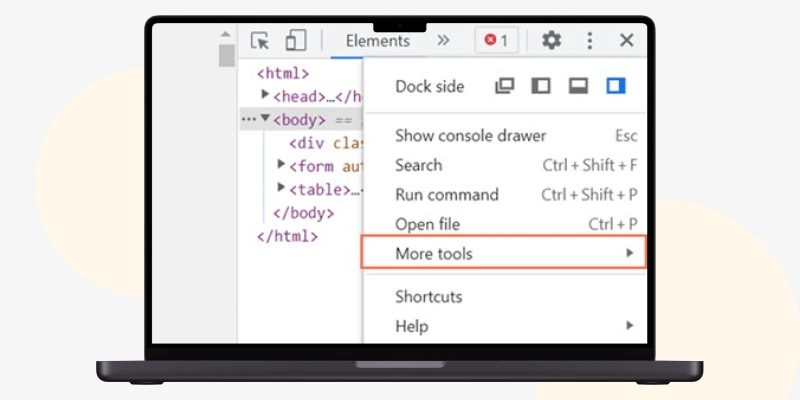
Next, simultaneously press the “Alt + F” keys and select “More tools” followed by Developer tools.”
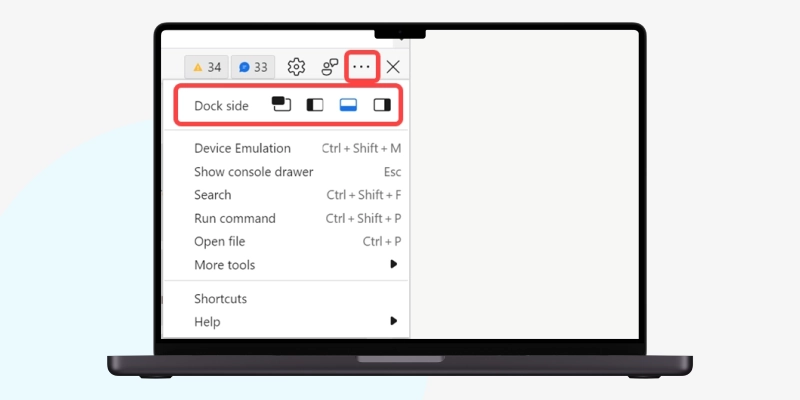
You can adjust the height by dragging and clicking on the three-dot horizontal icon on the developer tools menu bar to change its position to the top or bottom or to open it in a new window.
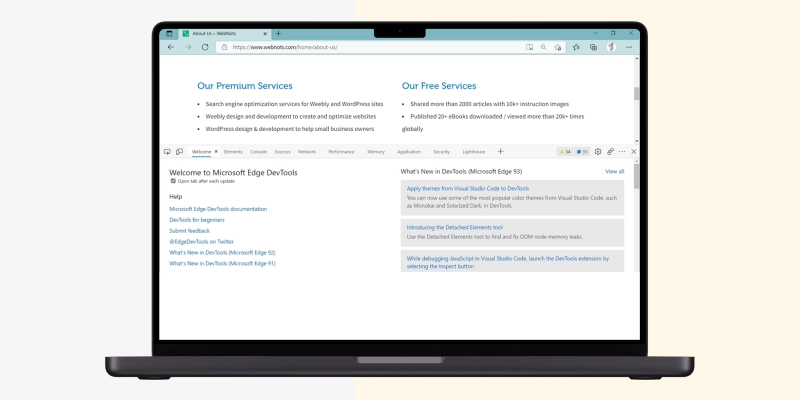
Though DevTools has many menu items, you must use only a few to analyze Edge's website source code.
Click below to learn how to inspect HTML source code!

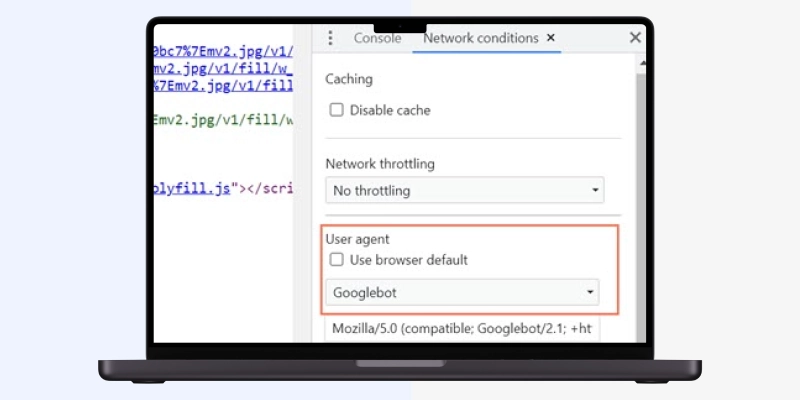
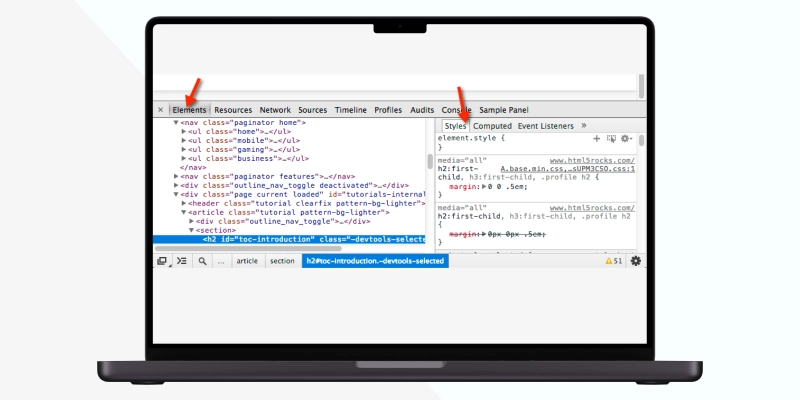
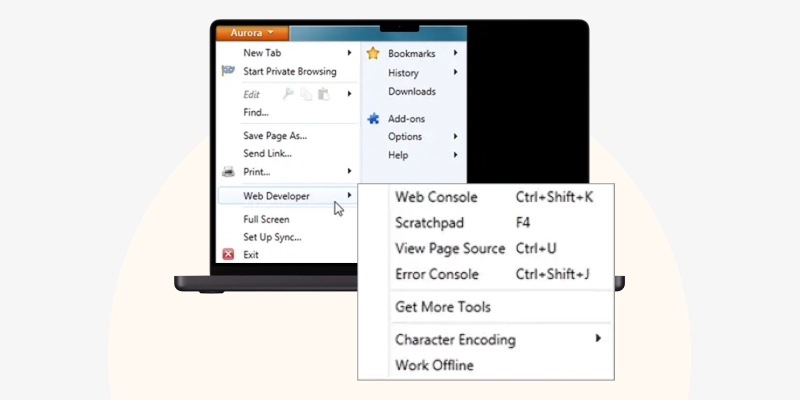
You can use Google Chrome's developer tools to view your page's source code like search engines do.
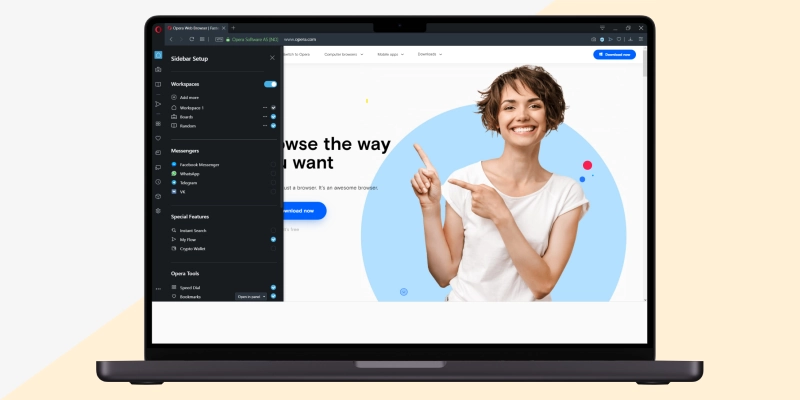
For Opera - Press CTRL + U. You can also right-click on the webpage and select “View Page Source.
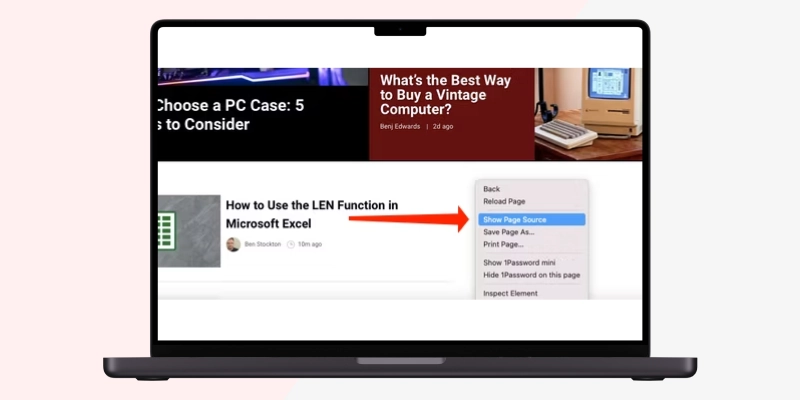
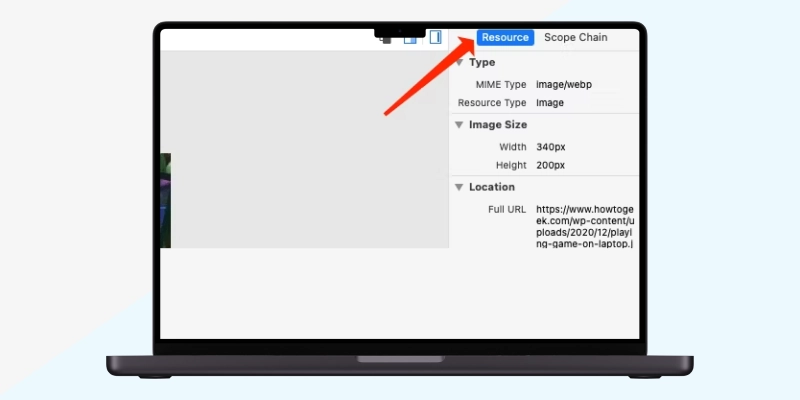
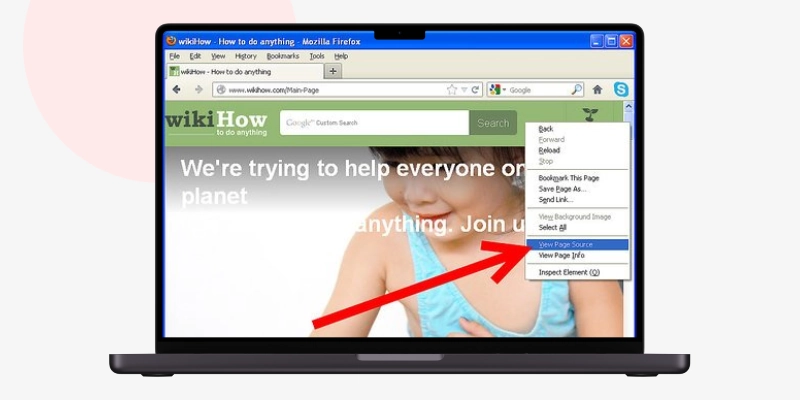

You also can right-click and select “View Page Source.” The keyboard shortcut is Option+Command+U.
Simply put, the set of instructions written by a programmer in a programming language, such as Java, PHP, Python, etc., to command a website to behave a certain way is the “source code.” Sometimes, coders may add notes or commentary along the code’s length to help the developers streamline the website creation process.
Source code is considered as much a copyrightable intellectual property of the creator as any piece of literary work. Although viewing the source code is not an offense per se, copying it entirely or as a whole is. However, since copyrighting demands transcribing the entire work in documentation, which can fall into the hands of malicious elements, developers use patent and trade law to protect the secrets of their code. Various other remedies exist for source code protection, including:

Suppose you, as a developer or a website owner, suspect plagiarism of your site’s source code. In that case, you can claim damages after proving that your site has been copied, used, translated, or exploited without your consent.
Your website’s source code can impact its SEO performance, user experience, and security. Viewing source code can be a preliminary audit for any performance lags, supplemented with a tool to probe deeper.
You can also “reverse engineer” your competitor’s source code to check and compare the features of their websites. If you’re unsure which features you can check, here are some starting points:
Title tags are HTML codes that enable you to give your web page a title. Since they play a decisive role in helping your website rank on search engines, not including them or creating them poorly could lead to SEO issues.

Your title tag and meta description would look something like this on Google Chrome:

Additionally, you can follow the steps for viewing source code on Chrome to analyze the title tag as shown below:
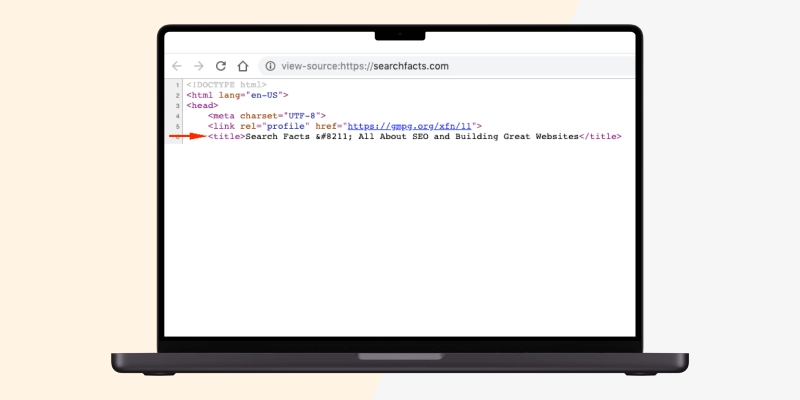
Your site's URL, hN tags, ALT attributes, title tags, meta descriptions, and inbound and outbound links contribute to its SERP performance.
Another SEO essential is a meta description within your HTML code's head section. Meta descriptions outline what your site visitors can expect upon clicking a link. Thus, meta-descriptions are the “deciding factors” on which your site’s page view sessions or bounce rates hinge. Make sure that all your web pages have a meta description, but they are not duplicated across the board. Some additional points to consider include:
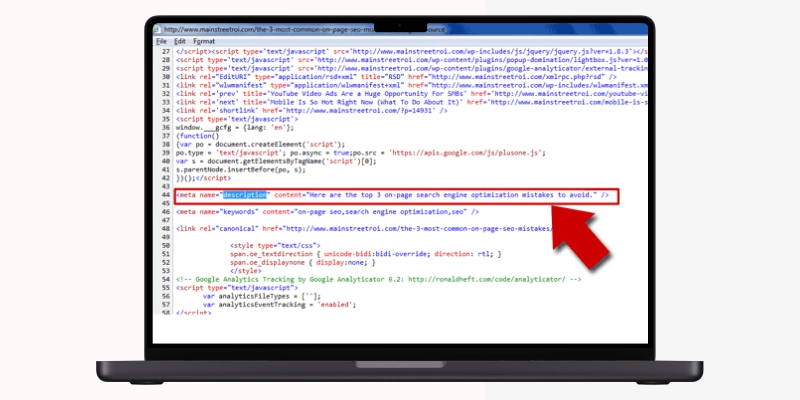
When all’s well, your meta description should appear like this in Chrome’s source code.
Click on “Dev Tools” and check the following elements on your website to ensure they are secure.
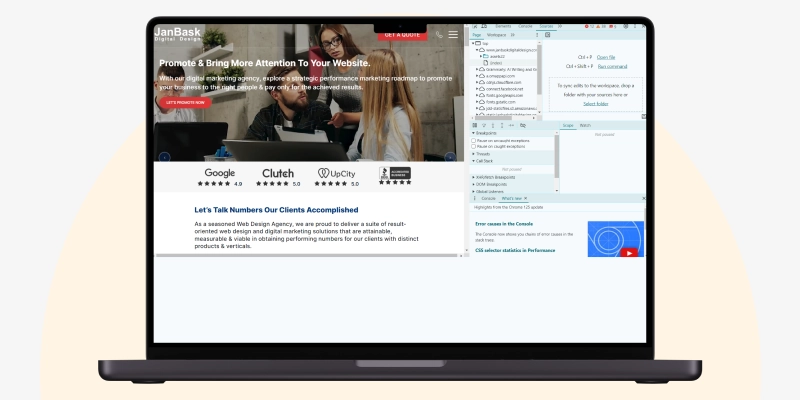
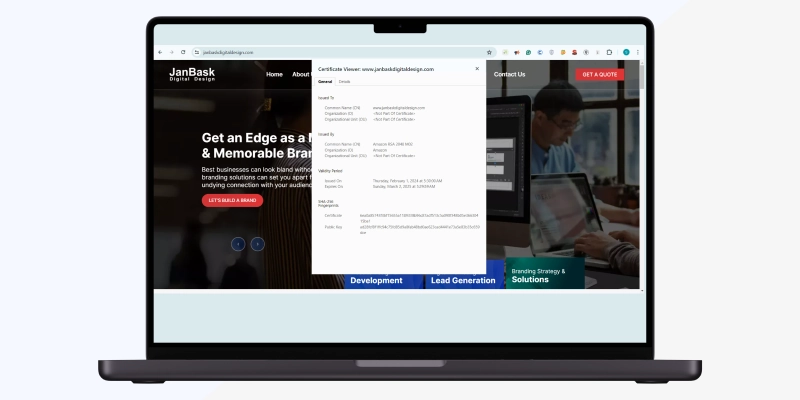
You must know Document Object Model specifications for HTML and XML documents to confirm that your site’s elements look exactly how you want them to. DOM elements are a breakdown of the page’s source code from the user’s point of view. You can check the web page's source code to access the DOM tree and its subsequent DOM elements.
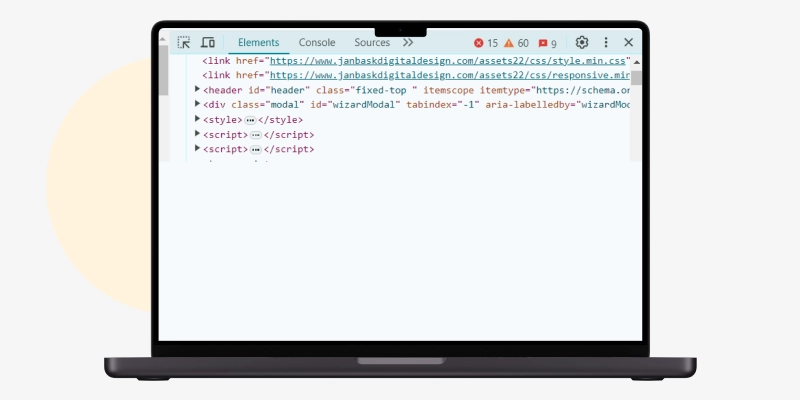
If you note that a particular section does not render properly in the DOM, you can have it fixed.
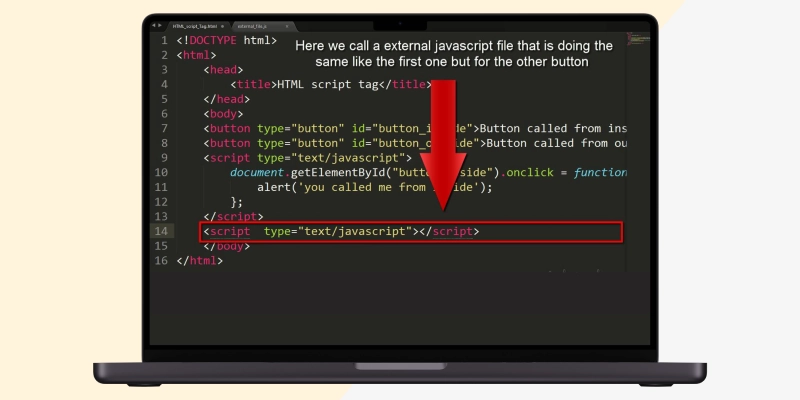
Although you may want to add scripts to your web page to boost its functionality, you must know that adding too many of them can slow your page’s loading time, thus increasing your bounce rate. Ensure the following parameters when it comes to scripts on your website:
This is how your HTML’s script looks on the web page source
Check your HTML’s “display: none” property to see files that should not be hidden but still are. Usually, these files are combined with Javascript or SEO specialists to boost your site’s ranking and functionality. Sometimes, content gets mistakenly hidden. However, hidden content can emanate from plugins installed by dishonest agents to enable your site to manipulate search engines for ranking better. Also, CSS can be manipulated via:
How can you check these hidden files to ascertain whether or not they are malicious? Simple, view your source code and then press the following:
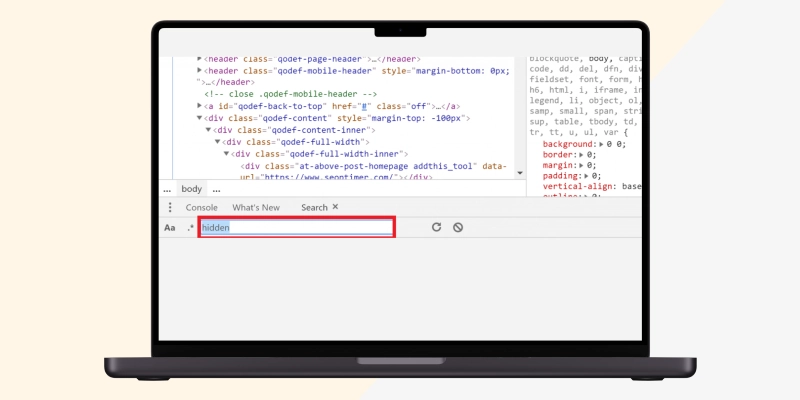
Enter "hidden" or "display: none" in the search bar to reveal all hidden files. If this function/style is unwanted, consult your developer to reverse it.
Yes indeed! You only have to access the Android Open Source Project(AOSP) repository, where the Android source code is on Git. On the other hand, however, it can be examined online or downloaded onto any individual personal computer to view it more clearly and even achieve some modifications if necessary. It is a limitless path for anybody interested in creating new content on the site. This can be interpreted in several ways, as there are diverse opinions regarding how this technology can be used.
AOSP grants various methods for finding the source code, including using Git instructions on their portal. First, one duplicates the store to a nearby drive, after which they can select what they wish from it before downloading this repository. Otherwise, you may surf this database at their online portal site at developers.android.com/open-source.
In addition, Android Studio, the official integrated development environment for Android application development, possesses features for viewing and navigating the source code of Android applications. Thus, you can analyze the source code of Android apps with Android Studio, look at various files, and understand the project structure and how the app was created.
Apple’s closed ecosystem policies make it difficult to access the source code on an iPhone. Unlike Android, viewing the iOS source code directly is impossible. Nevertheless, reverse engineering tools such as class-dump or Hopper Disassembler may be used for third-party iOS application analysis. By doing so, developers will get an in-depth understanding of how these apps are built, thus revealing the code structure or functionality (inside). Note that reverse engineering must be done legally.
To see the source code that Google uses in its products, you can use public open-source repositories that Google maintains on sites like GitHub or its public repositories. For example, Github hosts numerous Google-released projects, including highly demanded ones like TensorFlow and Chromium. Examining these repositories allows you to understand the code base, work with more programmers, and improve any project.
Decompiling an APK (Android application package) extracts the source code. Specialized tools such as JADX or Apktool convert the compiled bytecode into code humans can read. By doing this, developers can examine the Android app's underlying source code, giving them a better understanding of how it works and how it’s organized.
Getting the source code of a mobile application usually means finding the various procedures of contacting the application maker to ask for access or checking if it is available under some free software license (open-source). When the app falls into the open source category, you may find all required codes on GitHub or GitLab, among other platforms usually available to the general public. On the other hand, someone may employ very sophisticated methods of extracting these codes through reverse engineering processes in cases where the app was closed off during its creation, specifying only basic functionalities or containing some bugs/errors.
You may use open-source software in your application as the open-source license outlines. Since some (licenses) contain specific requirements for assignment/distribution/alteration, it is necessary to carefully read and truly understand each item contained within your favorite type of license file.
Now that you clearly understand the source code, how to view it, and its legal ramifications, you can routinely use its access to improve your site’s performance. With Chrome’s DevTools, you can leverage endless possibilities to redesign and refine your site for maximum performance. Viewing your page source code at a glance can help you perform a preliminary SEO, UX, cybersecurity, and other types of audit. However, you need to contact an agency specializing in these services for a more comprehensive deep dive of an audit into your site.
Interested in our Web Development Services!

Leave a Reply